Relational and Boolean Expressions
-
Boolean expression is an expression that evaluates to a Boolean value (true / false) and is commonly used for conditional rendering and logic handling.
-
It can be produced by relational operator, equality operators, logical NOT (!) and conditional operator (? :) (Boolean - JavaScript | MDN, n.d.).
-
-
Relational expression use relational operators and operands of various types to evaluate to some Boolean representation.
-
Relational operators have two categories:
-
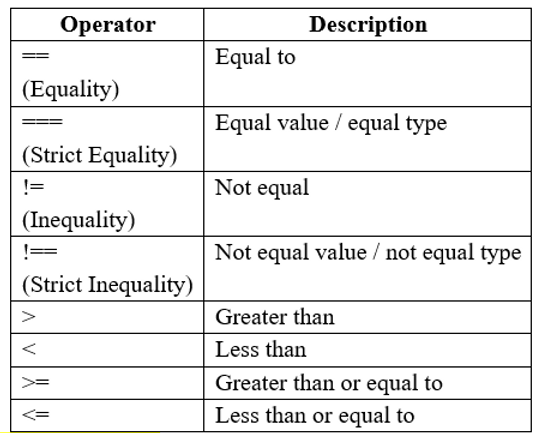
Comparison Operators:
-
Used in conditional statements to compare values and take action on the result (JavaScript Comparison and Logical Operators, n.d.):
-
-
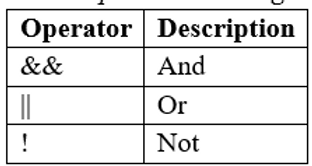
Logical Operators:
-
Used to determine the logic between variables or values (JavaScript Comparison and Logical Operators, n.d.).
-
-
All relational operators return a Boolean value (Comparisons, n.d.):
-
True – means “yes”, “correct” or “the truth”
-
False - means “no”, “wrong”, or “not the truth”
-
-
Short Circuit Evaluation
-
Short circuit evaluation (minimal evaluation) is an expression in which the result is determined without evaluating all of the operands and/or operators.
-
A technique used to improve performance in Boolean expressions.
-
Short-circuit evaluation in React.js allows for more concise and potentially performance-enhancing code, by ensuring that the second part of an AND (&&) operation is not evaluated if the first part is false (The Short Circuit Evaluation. And How You Cant Use It in React… | by Vitor Britto | Medium, n.d.).
-

Sample Code for React.js in our sample application:
Relational Expressions
-
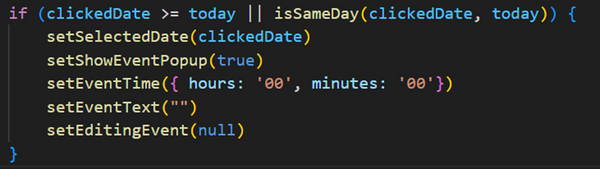
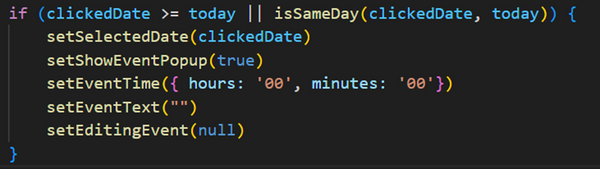
Conditional Check: The if statement ensures that the selected date (clickedDate) is either today or in the future.
-
clickedDate >= today: A relational comparison checks if the selected date is later than or equal to the current date.
-
isSameDay(clickedDate, today): This additional check ensures that clicking on the current day is also valid.
Logical Expressions
-
The >= operator ensures that the selected date (clickedDate) is today or any future date.
-
The || (logical OR) ensures that if the date is the same as today (isSameDay(clickedDate, today)), the condition will still be true.
-
If either condition is true, the block of code inside the if statement is executed.
Boolean Expressions
-
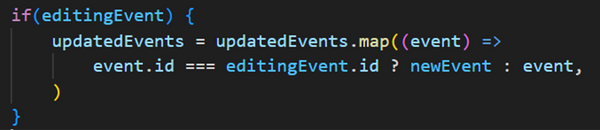
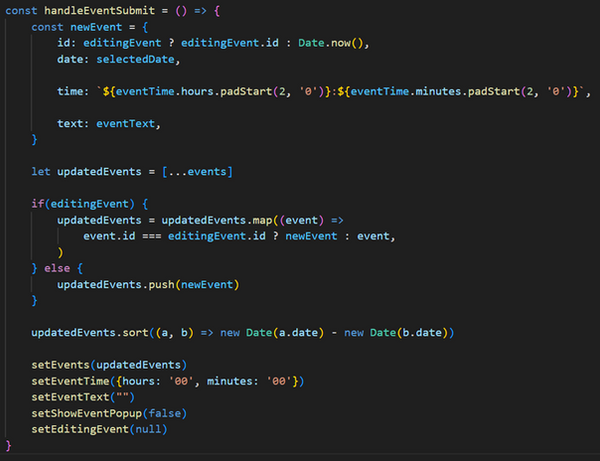
The editingEvent state is used to determine whether the user is editing an existing event or adding a new one.
-
editingEvent ? editingEvent.id : Date.now(): If editingEvent is not null, it uses the existing event's ID; otherwise, it generates a new ID.
-
if (editingEvent): This block checks if editingEvent is truthy, meaning an existing event is being edited. If not, a new event is added.
Short-circuit Evaluation
-
Condition Check: The if (editingEvent) ensures that the code inside this block runs only if editingEvent is not null or undefined. This means the user is currently editing an existing event.
-
Logic Inside: When editingEvent exists, the app updates the events array by replacing the existing event with the updated one (newEvent).